Onion nematode - description, photo, available methods of struggle
Content:

Onion nematode affects not only the culture to which its name is confined, but also garlic. The worm settles in the bulbs, lays its offspring in them, which in turn becomes the cause of the deformation of the outer parts of the plant, the drying of the root system. Timely identification of the pest, carrying out preventive and destructive measures will help to cope with a dangerous parasite.
Parasitization of the onion nematode
Nematodes are an extensive family of parasitic roundworms. The taxonomists discussed for a long time about the species of this parasite. Earlier onion stem nematode and potato were classified as one species, but several decades ago it was still revealed that pests have different food objects.
The parasite is widespread everywhere, it is not present only in the Far North, in Antarctica and in the tropics. In the Russian regions it is found mainly on heavy soils. According to experts, 25% of onion crops and 35% of garlic are infected with a nematode.
How to recognize an onion nematode
The length of adult worms varies between 1.1-1.8 mm. Width is from 20 to 40 microns. Females are larger than males. A thin body becomes slightly concave when heated, gradually tapering from two sides. In the photo of the onion nematode, you can see that the final part is cone-shaped.
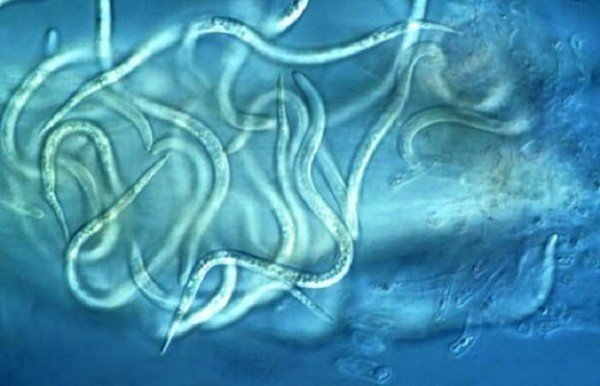
Newborn larvae from adults are distinguished by an inferior reproductive system and miniature dimensions - only 0.3 mm in length. Larvae of the last fourth age grow to 1-1.28 mm. The eggs are really tiny 70 × 30 microns.
The nuances of life
A population of nematodes can dwell in the ground and patiently wait for the host plant. In search of food supply, they are able to rise from a depth of 1.5 m. Adult individuals attack stems, leaves, bulbs, do not neglect seeds, and penetrate through stomata. The onion nematode mouthpart is a stylet with which the worm punctures plant tissues, injects its enzymes and absorbs the contents. Mass infection of the plant with parasites leads to the destruction of the part in which they settled. Nematodes are very picky about food quality. Dead tissue is not to their liking, so they leave the destroyed areas and migrate to the next part of the plant.
On a note! For their tiny dimensions, onion stem nematodes are notable for good sprinting qualities. They overcome the distance of 5 cm in 1.5 hours.
Breeding
Mating of mature individuals occurs directly in the host plant. During its short life of 30-45 days, the female lays up to 400 eggs. She makes it dosed: 8-10 eggs per day. The optimum temperature for laying offspring is 13-18 ° C. But even in the temperature range from + 1 ° С to + 35 ° С, the reproduction of onion nematodes does not stop.
Under favorable conditions, after a few days, larvae hatch from the embryos. Young individuals need nutrients and begin to actively eat, absorbing the tissues of the plant in which they are located. Larvae of older ages are less attached to the donor and, with a lack of food, can move to neighboring plants. As they grow older they undergo 3 molting and after 2 weeks become adult sexually mature worms. Having become an adult, already for 3-4 days the female begins to lay eggs. 6-8 generations of offspring are possible per season.
In one bulb, the number of nematodes amounts to thousands. So, as a result of the study, about 15 thousand worms were recorded in only one plant.
Tenacious parasites
Onion nematodes are characterized by amazing survival:
- parasites remain viable when storing bulbs in vegetable stores, at a constant temperature of + 2-4 ° C, only about 20% of the population dies, the rest remain viable;
- eggs and larvae can withstand low temperatures up to minus 80 ° С for 20 minutes; therefore, it is not surprising that cold winters do not reduce the number of pests in the soil;
- without food in the soil, onion nematodes live up to 18 months;
- at low humidity, individual individuals fall into suspended animation, in which they can stay up to 20 years;
- in plant residues, the viability of nematodes lasts from 6 months to 3 years.
Heavy soils, high humidity, the presence of a food base are ideal conditions for the preservation of a population of stem onion nematodes.
Symptoms of infection with onion nematodes
External signs indicate the invasion of plants by onion nematodes:
- deformation and drying of green mass;
- the bulb acquires a friable structure, cracks, the bottom easily separates;
- after rain, a characteristic smell of rotten onions may be felt in the area.
When the crops were infected in the late stages of vegetation, parasitization of the onion stem nematode gives white spots on the bulbs. Cutting them, you can notice granular thickened flakes. Depending on the degree of infection, their color changes from white to gray, brown. The onion becomes soft to the touch. The bottom and sides often crack, and cavities form inside.
Often the disease is spread by foci. On the site, planted with onions, changes and deterioration of the state of crops can be noticeable only in certain places. The parasite population is affected by their initial number, weather conditions, the amount of moisture, and the resistance of the culture to pests.
Onion nematode chooses garlic as an object of nutrition and reproduction. In an infected plant, the false stem takes on more thickened forms and cracks. The leaves curl in waves, turn yellow prematurely, and the underground part of garlic becomes excessively moist and rotten.
Malware
Parasitization of the worm onion negatively affects productivity. Infection at the planting stage greatly slows down and reduces the germination of bulbs. Shoots appear later, lag behind in growth, and often die.
The introduction of nematodes causes the development of fungi and bacteria in plants, which in turn leads to their weakening and reduces resistance to other pests.
In the fields, nematodes of onions and garlic are most actively manifested in late August.
No less harm is done by infected bulbs that have fallen into the vegetable store. In the absence of proper storage conditions, the worms continue active development and reproduction.
The harmfulness threshold of onion nematodes is 20 individuals per 1 kg of soil. If so many pests were found in the soil, cultivating the crop in this area is not recommended. Diagnosis of soil is carried out after harvesting and before planting. As the samples for analysis, the earth itself and the root tissue of the plant are used directly.
Ways to deal with a dangerous parasite
The stem nematode penetrates into plants from the soil, in which it is reliably protected from the negative effects of the external environment, from plant debris, stock, tools, with seed. As with other types of nematodes, fighting a parasite is very difficult. This is due to its microscopic size, difficulty in detecting in the early stages of infection, and high survival.
Of great importance are preventive measures that help reduce the spread of parasites. These include:
- disinfection of sown areas;
- primary scrupulous selection of healthy planting material immediately after harvesting and secondary before sowing;
- disinfection of inventory;
- timely removal and burning of plant debris after bulb harvesting;
- regular weeding and eradication of weeds, which may be a temporary habitat for parasitic worms.
Compliance with crop rotation with an interval of 4-5 years will significantly reduce the chances of preserving the onion nematode population.
It is recommended to avoid planting seeds, bulbs in high humidity and warm temperatures. It is precisely at such periods that the peak of onion nematode infection occurs. The optimal conditions for sowing events are permissible low temperatures and low humidity.
As a prophylaxis of the nematodosis, peat and sand are added to the soil so that it becomes more loose. To improve its condition and ability to retain moisture, nutrients add natural fertilizers. Also, if necessary, the soil is deoxidized with dolomite flour, scattering it on the surface before digging.
An effective folk remedy that helps prevent the appearance of onion nematodes is to till the soil before sowing soda solution. To do this, mix water and baking soda in a ratio of 1 liter of water per 1 g of food additive. The resulting mixture was watered at the rate of 3 liters per 1 square. m
Effective treatment against onion nematodes
There are several ways available to deal with onion nematodes:
- To control parasites in the spring, soil treatment with chemicals is carried out. Against parasitic worms, the recalcitrant percalcite is well established. The drug destroys larvae and eggs. 7-10 days before sowing in dry weather, the product is evenly distributed on the planting areas (200 g per 1 sq. M), then with the help of a shovel or rake it is applied to the soil to a depth of 10-15 cm. Urea, ammonia water can also be used. .
- To destroy parasites on the bulbs, they are filled with water (temperature 45 ° C) and left for 1 hour, then dried and planted.
- To disinfect planting material, it is kept for 2 hours in infusion of wood ash.
- For the same purpose, the bulbs are heated for 10 hours at a temperature of + 42 ° C.
To clean the bulbs from nematodes, a solution of potassium permanganate 0.05% or formalin 0.5% is prepared and planting material is kept in it exactly one day. According to the same principle, one percent saline solution is used.
How to store onions
Before laying the crop in the vegetable storehouse, fumigation is carried out - cleaning and disinfection of the room. To do this, you can invite sanitary workers or carry out the procedure yourself using sulfur dioxide: 50 g of sulfur per 1 sq. Km. m square for 24 hours.
Before storage, the bulbs are subject to a thorough inspection. It is important that the humidity in the storage does not exceed 65-70% and the air temperature is maintained within + 2-3 ° C.
Onion nematode is a dangerous pest. Only by observing rotation of the crop rotation, disinfecting planting material, it will be possible to preserve the crop and protect it from parasites.


 (votes: 5, average rating: 4,00 out of 5)
(votes: 5, average rating: 4,00 out of 5)