Encephalitis tick - how does a dangerous virus manifest?
Content:

The risk of contracting a serious viral disease - tick-borne encephalitis is not thought of by everyone relaxing in nature. This is due to a lack of information about the disease, methods of infection, symptoms and preventive measures. About 400 thousand cases of suction of ticks are recorded annually. Upon examination, the virus is detected in 4-6% of those bitten. The encephalitis tick is active in late spring when a stable warm temperature is established. Care should be taken in forest areas at this time. To protect themselves and children, doctors recommend vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis.
Disease carriers - who to fear
Outside the city, in dachas and in forests, people are in danger in the form of small blood-sucking parasites. They hide in tall grass and on the leaves of trees, waiting for a potential host. The main danger of ticks is the spread of many diseases: borelliosis, relapsing fever, tick-borne encephalitis. The latter ailment leads to serious disorders of the nervous system, and in some cases to the death of a person.
Attention. There are two ways of infection with the virus - transmissible (tick bite), alimentary - eating raw milk of goats or cows of carriers of the disease.
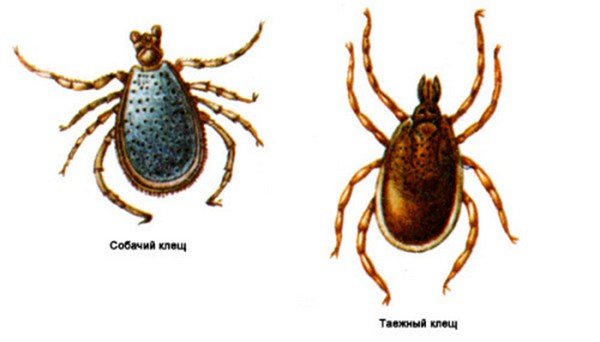
The carriers of the tick-borne encephalitis pathogen are ixodid ticks Ixodidae. There are up to 650 species, in Russia they are dangerous taiga and a dog tick. The first species is widespread in the forests of Siberia, the Urals and the Far East. The second is in the European lane. In late spring and early summer, their number reaches peak marks, so the number of bites increases sharply. The virus is carried by adults, nymphs and larvae. Not only people, but also animals become victims.
Attention. Despite the name of the species - a dog tick, the parasite attacks the other animals with equal frequency, as well as humans.
What does an encephalitis tick look like?? The parasites have a rounded flat body of brown color. Females differ in larger size - 3-4 mm, males no more than 2-3 mm. Females in adulthood are covered with a chitinous carapace on a third of the back, and the back of males is completely closed. The parasite has 4 pairs of legs with suction cups that allow you to move on a vertical surface. The female lays up to 17 thousand eggs, but a small part of the offspring survives. Ticks go through several stages of development:
- egg;
- larva - eats once on small rodents;
- nymph;
- adult individual.
The transition from one phase to the next is accompanied by molting. At the end of summer, nymphs become sexually mature, fed up with blood, females mate with males and lay eggs and die. Males die immediately after fertilization.
Attention. The female can be on the human body for up to 2 days. It gets drunk with blood and grows to a size of 10 mm. The color of the swollen body changes to light gray.The male sucks blood for 4-5 hours, then falls off, its size does not change significantly.
How does a tick bite?
The bite of an arthropod does not cause pain, so a person does not notice it. The predator injects a special anesthetic into the blood. The individual penetrates deep into the skin, gradually plunging into the epidermis. To do this, she selects areas where blood vessels are closest to the surface. The structure of the proboscis and jaws of the arthropod predator is specially designed to easily dig into the skin and suck out the blood of the victim.
To suck, the parasite needs an open area of the body, it easily climbs under clothes. There are several places on the human body where the parasite is sucked in most often:
- neck;
- the area behind the ears;
- scalp;
- armpits;
- lower back;
- stomach;
- groin area.
Attention. The risk of a virus entering the human body increases in proportion to the parasite staying on the body. If the contact time is 24 hours, then the risk of infection is 80%, while if a parasite is detected after 1-2 hours, the risk is minimal.
An encephalitis tick bite leaves redness and inflammation on the skin due to an allergic reaction and microtrauma.
How to remove a tick
If during the examination a sucking parasite was found on the human body, it must be removed. To do this, you can use the means at hand:
- cosmetic tweezers;
- strong thread;
- special tool for removing the tick (sold at the pharmacy).
The main thing is to get the individual completely with the proboscis, without crushing the abdomen. It is necessary to capture the tick as close to the surface of the skin as possible. Pull out by turning counterclockwise. So the spiral proboscis comes out easier. When using the thread, a loop is drawn, which is drawn on by the parasite. The two ends of the thread are also twisted clockwise, the loop rotates the body of the tick. Oil flooding is not advisable, the parasite dies from this, but for laboratory analysis for encephalitis he is needed alive.
Externally, it is impossible to recognize whether or not a tick is a carrier of viral diseases. It is placed in a glass jar and delivered to the laboratory within 2-3 days. If this is not possible, then burn. The wound is disinfected with alcohol or iodine. When the proboscis is separated, it is pulled out of the wound like a splinter.
Attention. It is not advisable to remove the sucking individual with your fingers, if there is nothing at hand, it is advisable to wrap them with a bandage or scarf.
Disease information
Tick-borne encephalitis refers to natural focal viral infections. It is accompanied by inflammation of the brain and spinal cord. Untimely initiation of treatment leads to neurological and psychiatric complications. The virus is divided into three subtypes:
- European - distributed in the western part of the Russian Federation, transmitted by dog tick, mortality - 2%, complications and disability - 20%;
- Siberian - found throughout Russia and North Asia, the source of infection is a taiga tick;
- Far Eastern - distributed in the east of the Russian Federation, in China and Japan, transmitted by the taiga species of ticks, the number of deaths is up to 40%.
Attention. Worse than other patients with encephalitis, patients over the age of 50 suffer.
The clinical picture of the disease of the European subtype includes two phases. The first lasts 2-4 days, it is characterized by loss of appetite, muscle pain, fever, and vomiting. Then comes relief for 7-8 days. After remission, 25-30% of patients have a second phase. It is accompanied by damage to the central nervous system, manifestations of meningitis and encephalitis (fever, impaired consciousness and motor functions).
The Far Eastern subtype is characterized by more pronounced symptoms. The rapid course of the disease often ends in death. Damage to the nervous system occurs after 3-5 days. There is no specific treatment for tick-borne encephalitis.Patients are hospitalized, they are prescribed maintenance therapy and corticosteroid drugs.
Encephalitis tick virus symptoms
The bite of a tick infected with encephalitis virus can lead to serious health problems. The incubation period of the disease is 7-14 days, in some cases it can last up to 30-60. At this time, you must carefully monitor your health, pay attention to the appearance of malaise. The time of onset of the first symptoms of the disease depends on the state of the body's defenses, with weakened immunity, the consequences encephalitis tick bite appear after 3-4 days. They are similar to ARI or influenza:
- temperature increase to 38-390;
- nausea;
- body aches;
- lethargy and lethargy;
- muscle pain in the shoulder girdle and neck;
- loss of appetite;
- violation of coordination.
Clinical picture
With a mild course of the disease, the symptoms are lubricated, not all of them are manifested. The disease has two phases, after some relief of the febrile symptoms, complications occur in the form of damage to the nerve centers and brain. How is encephalitis treated? To combat the causative agent of the disease, the introduction of immunoglobulins is necessary. These compounds synthesized from blood plasma inhibit the development of the virus and the release of toxic substances. After a few days, the patient's condition improves, meningeal symptoms subside. Treatment necessarily includes taking drugs for intoxication. For full recovery of health, it is very important to start therapy on time.
The final disposal of the consequences of the disease occurs depending on its severity. With a mild form, the residual effects disappear after a month, with an average - after 2-4 months. After a complex form, restoration will take several years.
Do not forget that ticks also carry other infectious diseases. One individual can infect a person at the same time with several diseases.
Encephalitis Vaccination
In itself, a bite of a small parasite does not harm people, the danger lies in the infections that it transfers. Among the ways to deal with the consequences of a bite, an important role is played by an encephalitis tick vaccine. In a vaccinated person, immunity is stimulated. Tick-borne encephalitis virus inoculation is inactive. It does not pose a danger to people, and the body learns to fight the disease and produce immunoglobulin.
Several types of vaccines are used in the country, they are divided by the age of the patients. Children are given special drugs designed for the age of 1-11 years.
Who should be vaccinated?
Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis is not a mandatory procedure. It is recommended for residents of areas with a high prevalence of encephalitis and those who are going to visit this territory. In Russia, these regions include Siberia, the Urals, the Far East, the Northwest region and the Volga region. This applies not only to rest in the country or in the forest, but also to work in agricultural areas, construction and surveys.
Vaccination can be carried out at any time, preferably before the peak tick season begins (April, May). The scheme of the event depends on the type of drug chosen. The standard schedule provides for the introduction of 3 doses - the first in the fall, the second in 1-3 or 5-7 months, the third in a year. Revaccination is carried out after 3 years.
Attention. Like any medical procedure, vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis can have contraindications. They include: a period of exacerbation of chronic diseases, general malaise, pregnancy, and an allergy to vaccination.
Precautionary measures
- To prevent ticks from getting on the body, you should carefully equip yourself before going to the forest. It is advisable to wear clothes with long sleeves that have tight elastic bands in the area of the hands, and a collar that protects the neck. Protect the head with a hood or hat. Pants tuck into high shoes, covering the ankles.
- It is recommended to choose clothes in bright colors, then a brown tick will be more noticeable when viewed.
- Special repellents that repel parasites should be applied to the body. It is most convenient to use sprays, as well as cream and lotion. For four-legged pets, collars are used. Improving the safety of the walk will allow the processing of clothing and travel accessories with acaricides - Bree-anticlesch, DETA, Taiga, Garden. These drugs kill a predator a few minutes after getting on clothes, so it does not have time to get to human skin.
- On a personal plot, it is recommended to mow tall grass, in which imperceptibly arachnid predators. Pesticide treatment of plants will significantly reduce the likelihood of a parasite.
- An excellent result in the fight against encephalitis gives vaccination against a dangerous virus. The vaccination lasts for 3 years. It will prevent complications when an active virus enters the body.
Compliance with preventive measures significantly reduces the likelihood of a bite of an encephalitis tick. If the parasite still sucks, then the best option is to contact a medical institution. In most cases, people are not in any danger, but precaution will keep you healthy in any situation.


 (votes: 17, average rating: 4,41 out of 5)
(votes: 17, average rating: 4,41 out of 5)